SyB V-1901
Antiviral Drug
Brincidofovir SyB V-1901: Intravenous Formulation
Overview
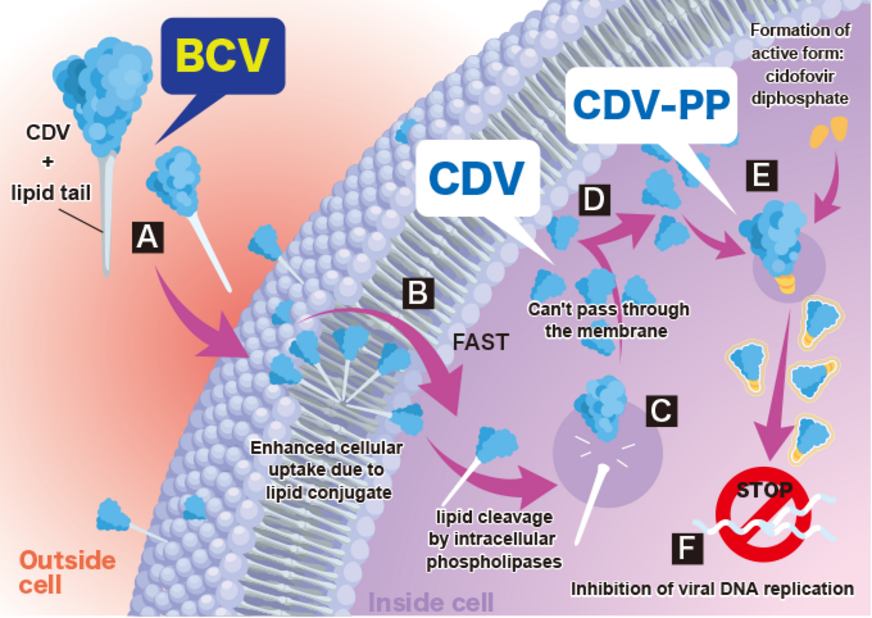
SyB V-1901 is an intravenous formulation of brincidofovir (“BCV”). BCV is a lipid conjugate of cidofovir (“CDV”, which is CDV is approved in the United States but not in Japan). Once inside the cells, BCV is converted into CDV-PP (CDV diphosphate), the active form of the drug. BCV exhibits significantly more efficient cellular uptake compared to CDV, resulting in higher intracellular concentrations. BCV has a high antiviral effect at lower doses due to the inhibition of viral replication by CDV-PP. BCV also exhibits a broader spectrum of antiviral activity than CDV or other antivirals, and is believed to be effective against a variety of double-stranded DNA viral infections, including cytomegalovirus, herpes viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), adenovirus, BK virus, papillomavirus, and smallpox virus and mpox virus. In addition, BCV is not associated with nephrotoxicity and myelosuppression, which are serious side effects of other antiviral drugs, including CDV.
Taking advantage of these characteristics of brincidofovir, SymBio Pharmaceutical is developing products in three therapeutic areas: post-transplant infections, blood cancers and solid tumors, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Leveraging the unique characteristics of brincidofovir, SymBio is developing the drug in three therapeutic areas: post-transplant infectious diseases, hematology and oncology, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Post-transplant Infectious Diseases
Adenovirus
SymBio is prioritizing global development of IV BCV for the treatment of adenovirus (AdV) infections in immunocompromised patients, such as those who have undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or organ transplantation. In March 2021, we submitted an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to initiate a Phase IIa clinical trial of IV BCV for the treatment of adenovirus infection, mainly in pediatric patients but also adults. In April 2021, the FDA granted fast-track designation for this development program. In May 2023, the trial showed IV BCV to be effective, establishing human POC (Proof of Concept). The Phase IIa trial completed in the first half of 2024, and we are currently in discussions with regulatory authorities in relevant countries to start a global Phase III clinical trial.
Cytomegalovirus
The Phase IIa clinical trial in the U.S. for patients with cytomegalovirus infection after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation began in May 2024. The first subject was enrolled in June 2024, and as of April 30, 2025, the cumulative number of subjects enrolled is 19.
Polyomavirus
Polyomaviruses, including JC virus (JCV) are dsDNA viruses known to cause severe brain diseases. Current antiviral drugs have limited effectiveness highlighting the need for the development of effective therapeutic agents. In November 2022, we entered into a Material Transfer Agreement (MTA) with Pennsylvania State University School of Medicine in the U.S. to conduct a non-clinical study to verify the antiviral activity of BCV in a mouse model of polyomavirus infection. In July 2024, the findings of the study showcasing the effectiveness of BCV were published in mBio.
○Hematology/Oncology
In addition to its high antiviral activity, BCV demonstrates anti-tumor effects. Through research collaborations with leading institutions around the globe, we are exploring BCV’s potential in indications in the fields of hematology and oncology.
We are collaborating with the National Cancer Centre of Singapore to investigate the anti-tumor effects of BCV on EBV-positive lymphomas and uncover its underlying mechanisms. Between 2022 and 2024, the findings from this joint research – covering the anti-tumor effects of BCV on NK/T-cell lymphoma, B-cell lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), and other lymphoma subtypes, as well on the identification of biomarkers predicting BCV’s efficacy – were presented at international conferences in both Europe and the United States on five occasions. In August 2024, SymBio initiated a global Phase Ib clinical trial in Japan in patients with malignant lymphoma. This trial, which is currently ongoing in Singapore and Hong Kong, is the First in Human (FIH) study of IV BCV in oncology and aims to establish the POC of BCV in the oncology area. In addition, in April 2023 we entered into a collaborative research and development agreement (CRADA) with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to evaluate the efficacy of BCV in EBV-related lymphoproliferative diseases.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
EBV and Multiple Sclerosis
In January 2022, Science reported that EBV infection plays a significant role in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS), an chronic and debilitating disease that affects an estimated 3 million people worldwide. Science also highlighted the potential of targeting BEV with antiviral drugs. Additionally, a series of reports published in Nature explored the relationship between EBV infection and the pathogenesis of MS.
In August 2022, SymBio entered into a Material Transfer Agreement (MTA) with the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Subsequently, in March 2023, we entered into a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with NINDS to conduct preclinical research with the objective of acquiring the necessary data to facilitate future clinical trials. In October 2023, the research findings were presented at the 9th Joint ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS meeting. Currently, this collaborative study is ongoing and involves use of marmosets.
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Alzheimer's Dementia
Certain dsDNA viruses, such as herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV), have a directivity toward cranial nerve tissues. A growing body of research indicates that reactivation of these latent viruses may have a role in the development of various neurological diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). In December 2022, we entered into a Sponsored Research Agreement with Tufts University in the United States to examine the effects of BCV on AD-like changes caused by herpes simplex virus infection and reactivation. The study uses a three-dimensional brain tissue model composed of human neural stem cells, developed established by Tufts University.
Other Collaborative Research
In addition, we are actively engaged in other collaborative research and development in the fields of viral infections, hematology and oncology, and neurodegenerative diseases with renowned research institutions worldwide. This includes collaborations the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke in the United States and Gustave Roussy in France. The outcomes of these efforts are regularly presented at leading conferences.
License
In September 2019, SymBio signed a license agreement with Chimerix, Inc. (Headquarters: North Carolina, USA) to acquire exclusive rights to BCV worldwide, including development, sales and manufacturing, for all diseases except orthopoxviruses (such as smallpox and empox). In September 2022, Emergent Biodefense Operations Lansing LLC, a subsidiary of Emergent BioSolutions Inc., which received the license for BCV from Chimerix, became our licensor.
BCV has also been designated an orphan drug for the prevention of adenovirus and cytomegalovirus infections in immunocompromised patients in the European Union.
